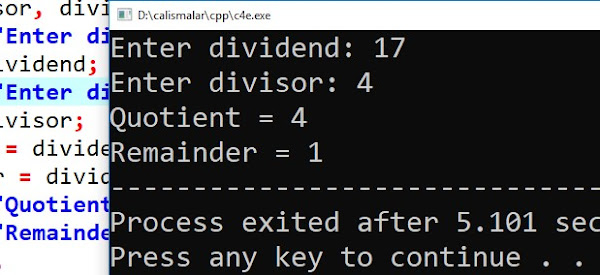
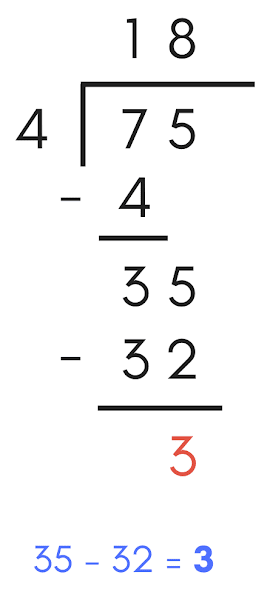Establishing the Issue Before you use a calculator to solve a division issue, it's a good idea to familiarize yourself with some fundamental words. The dividend is the number split into, the divisor is the number divided by, and the result is the quotient. Frequently, division problems are written as follows: Dividend multiplier equals quotient. If you phrase your division issue as a fraction, the dividend is the top number (also called the numerator), and the divisor is the bottom number (also called the denominator).
Long division with remainders is one of two hand-written ways for doing long division. It is somewhat simpler than solving a division issue by calculating the quotient using a decimal. Use our Long Division with Decimals Calculator if you need to do long division with decimals. What Are the Divisional Components?
As the numerator, use the remainder of the fraction (or the top number). The next step is to insert the fraction's divisor, or denominator, at the bottom. Multiply the quotient (or answer) by the divisor and then add the remainder to ensure that the result is correct. What is a rest in the context of long division?
Step I: Inside the bracket, write 94, and on the left side of the bracket, write 3. Step II: Begin division on the left and work your way to the right. Divide nine tens by three. We already know that 3 3 Equals 9. Substitute 3 for the quotient and 9 for the remainder. Subtract nine from nine. Step III: Remove four from their original locations. 3 becomes 4 once and leaves 1 as a residual. Subtract 1 from the quotient and 3 from 4. Thus, the quotient equals 31 and the remainder equals 1. To verify the solution, we use the following relationship: